1 - Cloud Concepts
MS Learn 25%-30%
Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet enabling faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
- It is easier to upgrade hardware, because you are no longer required to wait until the hardware you already have bought served it’s life sentence.
- You share certain costs with other tennents using the same cloud computing solution, which keeps the costs low(er).
Types of Cloud Solutions
- Private Cloud is a cloud solution used for a specific organisation.
- No Capital Expenditures to scale up.
- Applications can be quickly provisioned and deprovisioned.
- Organisations only pay for what they use.
- Public Cloud is a cloud solution owned by a cloud services or hosting provider. Provices resources and services to multiple organizations and users. Accessed via secure network connection (usually the internet).
- Hardware must be purchased for start-up and maintenance.
- Organisions have complete control over resources and security.
- Organisations are responsible for hardware mainenance and updates.
- Hybrid Cloud combines public and private cloud to allow applications to run in the most appropriate location.
- Provides the most flexibility.
- Organisations determine where to run their applications.
- Organisations control security, compliance, and legal requirements.
- Multi Cloud a company makes use of two or more different cloud providers.
Types of Expenditures
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
- The up-front spending of money on physical infrastructure
- Costs from CapEx have a value that reduces over time.
- Operational Expenditure (OpEx)
- Spend on products and services as needed, pay-as-you-go
- Get billed immediatly
Consumption-based model
Cloud service providers operate on a consumption-based model, which means that end users only pay for the resources that they use. Whatever they use is what they pay for
- Better cost prediction
- Prices for individual resources and services are provided
- Billing is based on actual usage
Cloud Benefits
- High availability
- Scalability You can scale-out or scale-in based on need (horizonal scaling). Add or remove a virtual machine/resource/node with the same services (identical copy). You would always need a load-balance to reach these nodes.
- Predictability There aren’t any surprise costs.
- Governance Easier to institute access management and other policies
- Elasticity You can scale-up or scale-out based on need (vertical scaling). Upgrade or downgrade the computing powers of a machine. This will require a reboot of the machine!
- Reliability The abilty of a system to recover from failures and continue to function.
- Security
- Manageability A lot of options to automate ops.
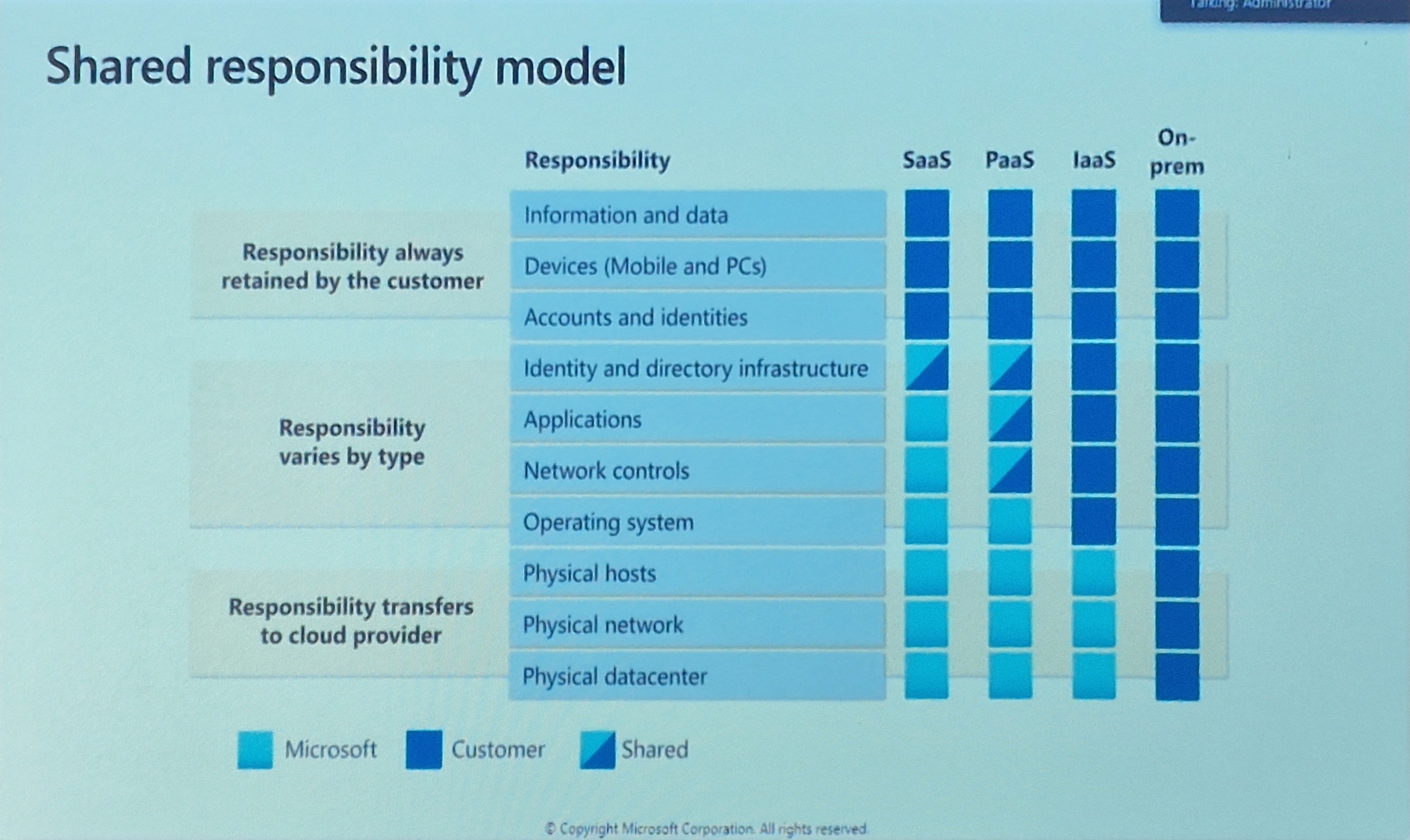
Cloud Service Types
- IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service
- Built pay-as-you-ho IT infrastructure by renting servers, virtual machines, storage, networks and operating systems form a cloud provider.
- The most flexible cloud serice.
- You configure and manage the hardware for your application
- Cloud provider is responsible for the:
- Physical building
- Networking, firewalls/security
- Servers and storage
- Built pay-as-you-ho IT infrastructure by renting servers, virtual machines, storage, networks and operating systems form a cloud provider.
- PaaS - Platform as a Service
- Provides environment for building, testing, and developing software applications; without focusing on managing underlying infrastructure
- Focus on application development.
- Platform management is handled by the cloud provider.
- Cloud provider is responsible for the:
- Physical building
- Networking, firewalls/security
- Servers and storage
- Operating system
- Development tools, database management, business analytics
- Provides environment for building, testing, and developing software applications; without focusing on managing underlying infrastructure
- SaaS - Software as a Service
- Users connect to and use cloud-based apps over the internet: for example , Microsoft Office, E-mail and Calandars.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing model.
- Users pay for the software they use on a subscription model.
- Cloud provider is responsible for the:
- Physical building
- Networking, firewalls/security
- Servers and storage
- Operating system
- Development tools, database management, business analytics
- Hosted applications/apps
- Users connect to and use cloud-based apps over the internet: for example , Microsoft Office, E-mail and Calandars.